Your tractor’s footprint is usually concealed by the towed implement, yet at a glance and in a matter of seconds it could help you detect, before the beginning of a campaign, a pressure irregularity or incorrect setting which could affect your soil. Excessive compaction beneath the tyre destructures the soil and prevents the filtration of water, air and nutrients.
Deep soil compaction is situated beneath the tyre and has a more general impact in the area around the tyre, i.e. a considerable part of the arable zone which is more or less thick depending on your region or your fields and will certainly have long-term repercussions on productivity in this zone.
1. The footprint is the best indicator of soil compaction
Your tractor tyres’ footprint is the visible side of the problem. It may be superficial or deep, depending on the type of soil, weather conditions, inflation pressure and total weight of your agricultural machinery.
Whatever the case, it allows you to determine, with a quick glance, the level of soil compaction in the wake of your tractor and potentially make the adjustments necessary to preserve your fields and future yields.
What is the impact of excessive compaction?
Soil is considered to be in perfect health when it is made up of 25% water, 25% air, 5% organic materials and 45% minerals.
But the effects of compaction beneath the tyres of your agricultural machinery inevitably lead to a destructuring of the soil.
When there is too much compaction, the consequences are as follows:
- The surface water infiltrates less easily, which reduces the deep reserves available during the dry season.
- The excess surface water delays the drying out of the soil in spring. This causes excess slip which slows down your work rate and destructures the arable layer of soil.
- Air has trouble circulating: the ground becomes harder, making biological life more scarce, such as the earthworms which help to trace the path of your crop roots.
- The efficiency of inputs is reduced: The water which can no longer penetrate stagnates on the surface, causing considerable leaching of inputs or phytosanitary treatments whose efficiency is diminished.
2. Weight distribution beneath the footprint
Analysing the footprint shows us the weight distribution beneath the wheel.
For example, weight is distributed more evenly under a radial tyre whose tread is laid flat on the ground, as compared to a bias-ply or diagonal structure tyre with a more rounded form, which has high pressure in the centre and low pressure directly above its sidewalls.
The weight distribution below the footprint depends on the tyre technology and the tyre’s internal structure
Radial tyres preserve your soil better thanks to a flatter, wider and more even footprint. The load bearing capacity is also spread out better thanks to its structure.
However, even with a radial structure tyre, there are major disparities in terms of pressure to the ground. Depending on the make of tyre and its internal structure, the pressure exerted on the ground will be different.
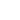
Below is a comparison of pressure to the ground caused by 6 different brands of tyre with the same dimensions.
They were fitted on the same machine with the same load and the same inflation pressure. We can see that the pressure transfer is directly linked to the tyre quality and technology.
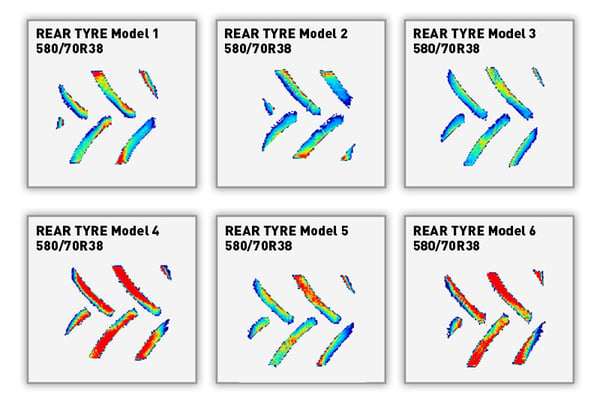
3. The depth of the footprint
The deeper the footprint, the more damage is caused to the soil.
If the footprint is visible after the implement has passed, this shows excess compaction. It’s a sign that the pressure is too high for your soil’s load bearing capacity.

Excess pressure can lead to the formation of ruts.
This problem accelerates soil erosion by channelling stagnant or run-off water in the ruts and prevents even irrigation of the land.
These ruts require soil restoration work which is not the cheapest solution, so it would be better to change to wider VF tyres which can work at low pressure and spread the load to the ground more evenly.
4. The length and width of the footprint
When you decrease pressure, the footprint gets slightly wider but much longer, which is difficult to see because the footprint follows in the trace of the tyre which is moving forward.
To see the length of the footprint, look at the tyre from the side; if a single vertical lug is in contact with the ground, the pressure is high.
When you reduce the pressure, two other lugs each side brush against the ground, so you have three lugs in contact with the ground when the vehicle is stationary, which gives you an advantage in terms of improving traction and avoiding slip. Rolling resistance will also be reduced, the tyre has a better grip on the ground and will sink less into the soil.
When in motion, the 3 lugs will act simultaneously. Driving with a low inflation pressure in the fields gives you a larger contact patch with the ground in the length of the footprint and improves traction. This allows you to transform vertical compaction into longitudinal compaction at the level of the lugs which is less damaging for the soil.
5. Comparison of VF tyre and standard tyre footprints

To compare soil footprints we used the same tractor equipped with the same implement, tyres of the same dimensions, inflated to carry exactly the weight of the implement in normal working conditions. Only the tyre technology is different, with Bridgestone VF VT-TRACTOR tyres on one side and standard technology tyres from another major competitive brand on the other side:

| Tyre | STANDARD | VF – VT-TRACTOR tyre | |||
| Tractor make/model | John Deere 6215 R | John Deere 6215 R | |||
| Tyre dimensions | Front = 600/70/R30 152 D | Front = 600/70/R30 165 D | |||
| Rear = 650/85/R38 173 A8 | Rear = 650/85/R38 179 D | ||||
| Load | Front = 3250 kg | Front = 3250 kg | |||
| Rear = 6810 kg with implement | Rear = 6810 kg with implement | ||||
| Pressure | Front = 1.4 bar > 3458 kg at 50 km/h | Front = 0.8 bar > 3300 kg at 50 km/h | |||
| Rear = 1.4 bar > 5180 kg at 50 km/h | Rear = 0.8 bar > 5100 kg at 50 km/h | ||||
| Footprint | Front = 643 cm² | Front = 737.03 cm² | |||
| Rear = 814 cm² | Rear = 905.81 cm² | ||||
| Depth of footprint | 93 mm | 60 mm |
We have two different technologies here, which show that the VF tyre has much less impact on the soil in your fields in the same working conditions.
The analysis of the footprints demonstrates that:
- The VF front tyre footprint is 15% larger than the footprint of the standard tyre
- The VF rear tyre footprint is 12% larger than the footprint of the standard tyre
- As a result, the VF tyre sinks 50% less deeply into the soil than a standard tyre.
6. The VF tyre for soil preservation with a longer, wider footprint
To obtain a wider, longer soil footprint, the best solution is to replace the standard tyres that were originally fitted on your tractor with VF technology tyres.
This type of top-of-the-range, low-pressure tyre has a reinforced casing with supple, resistant sidewalls which can work continuously at a pressure of less than 0.8 bar.
VF agricultural tyres are designed to avoid compaction. You will slip less, have less rolling resistance and better traction which will lead to fuel savings.
BRIDGESTONE VF VT-TRACTOR tyre footprint tests
By opting for a VF VT-TRACTOR tyre, for example, you ensure maximum soil protection thanks to a larger contact patch with the ground.
This tyre has a footprint that is up to 26% bigger than its main competitors.
BRIDGESTONE VF 900/60 R42 VT-TRACTOR tyre
We carried out tests that take into account the weight of the tractor, with its implement and load transfer, for a total of 21,440 kg, implement raised and load transfer to the front taken into account:
- The contact patch at a pressure of 1.8 bar is 1,260 cm²
- The contact patch at 0.8 bar increases to 1,719 cm²
- i.e. an increase in footprint size by more than 35%
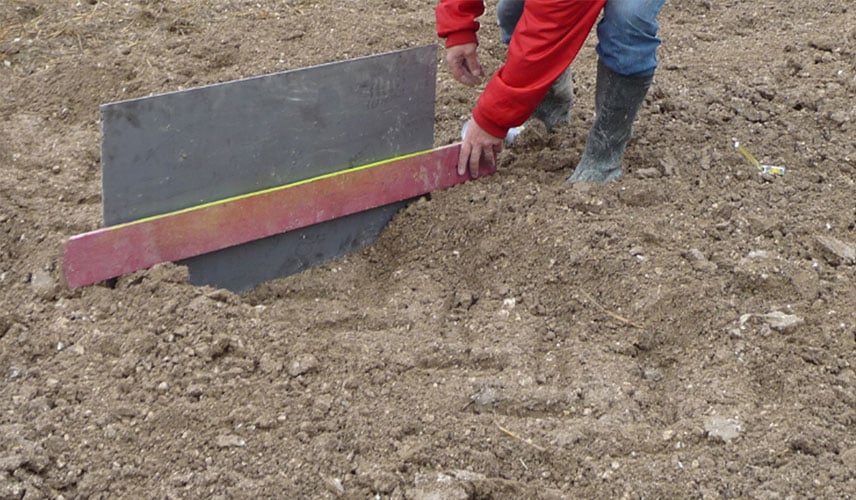
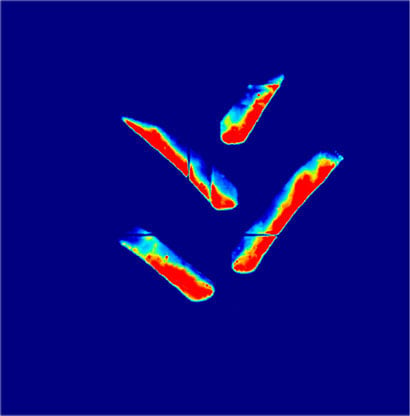
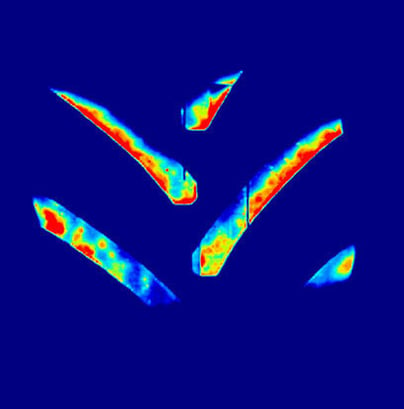
Below are images of the rear footprint with the implement down and the tractor stationary.
When in motion, the contact patch with the ground increases even more with the length of the footprint.
|
|
i.e. a contact patch that is more than 45% bigger at low pressure
with much less compaction in red beneath the footprint.
This allows you to cover about 1 hectare more during the day compared to a standard technology tyre, while preserving your soil.
The bridgestone-agriculture.eu blog is written and administered by tractor tyre experts who can provide you with advice to help you achieve optimum productivity (Technical data on agricultural tyres - Agricultural tyre performance - Advice on agricultural tyre pressure - Soil compaction prevention - Sprayer tyre pressure - etc.)
To take it a step further and increase your farm’s profitability, the blog Bridgestone-agriculture.eu has prepared a free, highly detailed ebook which explains the essential role of the agricultural tyre on your productivity.
Most people who read this article have also read some of the following articles:
- 9 major points on soil compaction linked to tractor tyres
- What you need to know about soil compaction caused by your tractor tyres
- Protect your soil during harvest for successful sowing in the future
- How to reduce soil compaction after harvesting?
- What are the consequences of the soil compaction caused by my tractor tyres?
- 3 soil conditions to understand to avoid compaction by your tractor tyres
- What type of farming tyre is best for preventing ruts?
- Expert opinion on soil compaction caused by tractor tyres
- Demonstration of soil compaction linked to your tractor tyres
This information is intended only to make you aware of the technical and functional aspects of agricultural tires and their use. It does not allow you to make a judgment or a definitive conclusion on a given problem. Only your agricultural tire expert is able to make a technical assessment and take a final decision, case by case.
Leave a
commentary
Your email address will not be published.
Required fields are indicated with *